Disability-Related Accommodations While Abroad

What Students Should Know
Student Accessibility and Accommodation Services (SAAS) is committed to helping disabled students participate fully in education abroad experiences. The University of Michigan wants you to feel informed, supported, and empowered as you explore your options. You may already have strategies in place for managing your disability on campus. However, your experience abroad may be quite different depending on your host country’s cultural attitudes, infrastructure, and legal protections.
It’s important to research the location where you’ll be studying to understand how your disability and accommodation needs may be affected. While accessibility abroad can differ from what you’re used to at U-M, staff within SAAS and our various Education Abroad offices are here to support your decision-making. We are here to help you gather accurate information and explore realistic options so you may ultimately make informed decisions that align with your goals and needs.
Understanding Disability in a Global Context
- In the U.S., disability is defined as a physical or mental impairment that significantly limits a major life activity, such as walking, seeing, hearing, breathing, learning, or caring for oneself. Accommodations in the U.S. are protected under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
- The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) does not extend to travel abroad; foreign institutions are not bound by it. Because of these limitations, U-M-approved accommodations cannot be guaranteed.
- Living in a different country with immersion in a new culture can bring challenges, including disability services and accessibility standards that may differ from those in the U.S.
- The likelihood of being able to use accommodations abroad may depend on how much control U-M has over various aspects of the experience, such as academics, transportation, and housing.
How to Get Started Exploring Accessibility Needs Abroad
Planning for accessibility abroad takes time and proactive communication. Here’s how to begin:
Step 1: Review Program Options
- Review program options either independently or with an education abroad advisor, such as those in M-Compass, and research general country information/attitudes around disabilities. Students can meet with education abroad advisors before or after applying for a program.
- Check the application and commitment deadlines and ensure that the program can meet your needs before confirming your participation.
- Review THINKING THROUGH TRAVELING ABROAD: Questions for Students with Disabilities to Consider
Step 2: Connect with SSD
See the flowchart below to determine the best next step depending on your own individual circumstances.
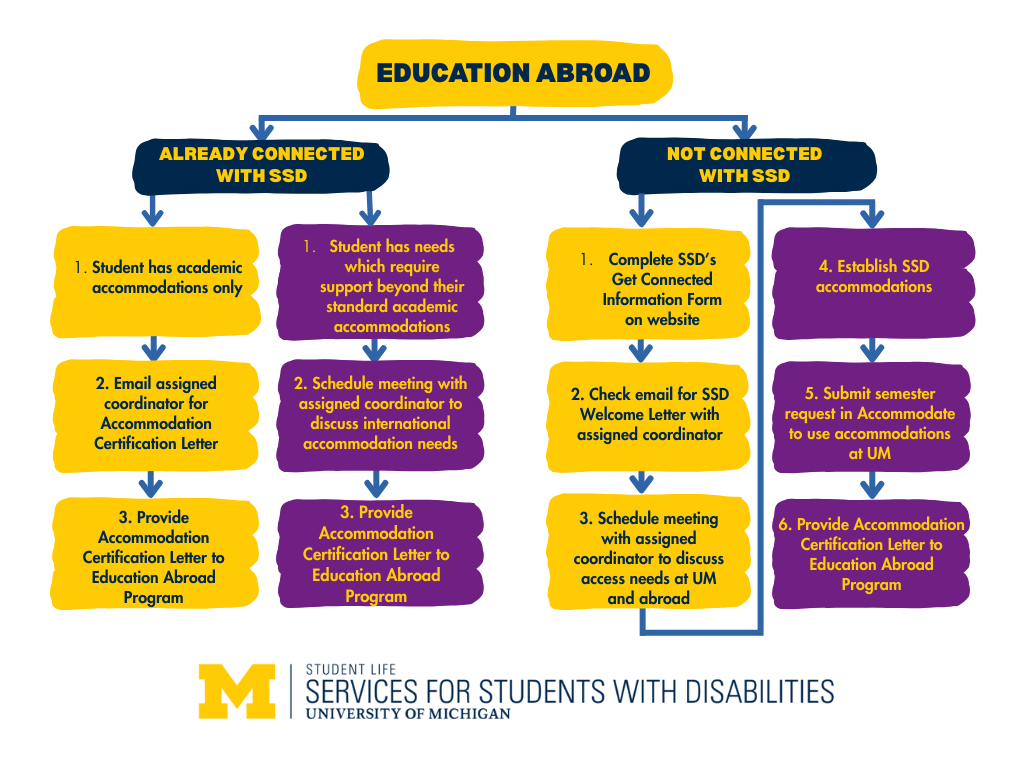
Step 3: Meet with the Education Abroad Advisor
- Students should schedule an appointment with their education abroad advisor/the office sponsoring the program in M-Compass to share their accommodation letter and discuss any disability-related concerns.
- Note: To determine whether your requested disability-related accommodations can be applied, you will need to contact your host institution. There are three ways to connect with your host institution:
- Request that your Education Abroad Advisor reach out on your behalf.
- Have your Education Abroad Advisor connect you directly via an introductory email.
- Have your Education Abroad Advisor provide you with direct contact information for the host institution or program leader.
For Students: Resources to Consider
- Explore U-M Education Abroad Opportunities
- Global Michigan’s Disabilities Abroad information
- Travel Health Preparation Guide
- U-M Travel Abroad Health Insurance
- Mobility International - USA
- Transitions Abroad - Disability Travel Abroad
- U.S. Department of State Accessibility Needs for Travelers
- UM Student Experiences Abroad
For Education Abroad Advisors/Host Institutions: Resources
- U-M Guidance for Education Abroad Advisors and Host Institutions
- Tips and guidance for supporting disabled students
- Thinking through traveling abroad: Questions for Students with Disabilities to Consider
